Molar Mass Of Dry Ice
- Air - What Is It?
- How to Detect the Molar Mass of Air?
- How To Theoretically Calculate The Molar Mass Of Air?
- How To Apply These Formulas In Practise?
- What Gases Are In The Air?
- Air Density
- Water Vapor
- Air Properties
Air surrounds united states of america every day, just we practise not notice it, although we cannot live without it. For humans, breathing is a reflex. We don't think near breathing, and we do it. Have you ever wondered what you know nearly air? If not, then our article volition get your door to the world of chemistry. Yous will learn how to find the molar mass of dry out air, the molecular weight of air, what a substance consists of, and many interesting facts. If yous detect it difficult to cope with a chemistry assignment, you lot tin always get our professional person homework help.
Air - What Is It?
Air Formula: since air is a mixture of gases, there is no formula.
The average molar mass: 28,97 g/mol.
The molecular mass: the molecular weights of CO2, H2O, and the atomic mass of oxygen are 44, 18, and 16 amu.
Solubilityof air in h2o: 29,eighteen cm3/l
How to Find the Tooth Mass of Air?
If this is your first time encountering such a task, there are ii methods you lot tin can use to fill up out the chemical newspaper correctly. Consider the first - you can calculate the tooth mass of air past adding the weight of each gas. Using the platonic gas equation, y'all can determine the molar mass of the gas. At not too high pressures but sufficiently high temperatures, the gas can be considered ideal. The Mendeleev – Clapeyron equation describes the country of such a gas:
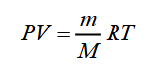
In this formula:
- P is the gas pressure;
- Five is the gas volume;
- m is the mass of the gas;
- M is the number of moles of the gas;
- R = eight,3145 J/(mol ∙ Thou) is the universal gas constant;
- T is the absolute gas temperature.
From the offset formula, we get the expression for the tooth mass of the gas:

Therefore, to calculate the molar mass of air, it is necessary to know the mass of the gas - grand, the temperature - T, the gas pressure - P, and the volume it occupies.
If the measurement errors of P, 5, and T in any experiment do not exceed 1%, so the determination of the gas mass is a difficult chore. Consummate gas removal from the vessel is almost impossible: even with the best modern engineering toolbox.
There is another way of determining M, in which it is non necessary to attain complete removal of the gas from the vessel - it is enough to alter its mass slightly. Allow a vessel with volume Five contain gas of mass m1 under force per unit area P1 and at temperature T. The equation of state for this gas volition take the form:
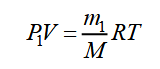
We pump out function of the gas from the vessel without changing its temperature. After evacuation, the mass of gas in the vessel and partial pressures will subtract. Let us denote them, respectively, m2, P2, and rewrite the equation of state:
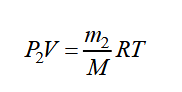
From the equations, we get:
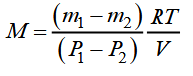
This expression allows you to decide - K. If the change in the mass of the gas, in pressure, the temperature, the volume is known.
In this piece of work, the investigated gas is air, known as a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, h2o vapor, and other gases. The above formula is also suitable for determining the M mixture of gases. In this instance, the found value of M is a certain average or effective tooth mass of the gas mixture.
How To Theoretically Summate The Molar Mass Of Air?
The molar mass of a mixture of gases (air), you can theoretically calculate. This method is suitable considering the relative content and molar mass of each of the gases included in the mixture are known. The formula looks like this:
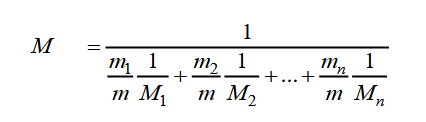
In this formula:
- m1/m, m2/k are the relative fractions of the content of each gas;
- M1, M - molar masses of gases included in the mixture.
How To Apply These Formulas In Do?
In chemistry homework, teachers give advanced data, gas percentages, diminutive weights, and different coefficients. Therefore, having all the information, you can apply the formulas. Let'southward take an example:
Task: Calculate the average molar mass of air has the following limerick: 21% O2, 78% N2, 0,five% Ar, and 0,5% CO2.
Decision: Since the volumes of gases are proportional to their quantities (Avogadro'south police force), the average molar mass of a mixture can be expressed both in terms of volumes and in terms of quantities of substances:
Mav = (M1 · V1 + M2 · V2 + M3 · V3 +) / (V1 + V2 + V3 + ...) (1)
Mav = (M1 ν1 + M2 ν2 + M3 ν3 +) / (ν1 + ν2 + ν3 + ...) (ii)
Take ane mol of air, then v (O2) = 0,21 mol, v (N2) = 0,78 mol, 5 (Ar) = 0,005 mol and five (CO2) = 0,005 mol. Substituting these values into the formula, nosotros get:
Mav (air) = (0,21· 32 + 0,78 · 28 + 0,005 · 40 + 0,005 · 44) / (0,21 + 0,78 + 0,005 + 0,005) = 29 g/mol.
That is why in numerous computational bug related to the relative density of gases in the air, the boilerplate tooth mass of air is always causeless to be 29 g/mol.
Respond: Mav (air) = 29 yard/mol.
What Gases Are In The Air?
Atmospheric air is a mixture of gases. However, this is not a complete definition, and to expand it, we turn to history. In 1754, Scottish physicist and chemist Joseph Black, while heating white magnesia, discovered the release of "bound air." Having received CO2, Mr. Black made some other significant discovery - the composition of the air, which was previously considered one substance, is not uniform.
Joseph Black showed the style to other scientists who, one after another, began to more and more than decipher the composition of the atmosphere, summate oxygen in the air, and other gases. The very definition was formed, which today sounds like this: air is a mixture of gases that form the Earth's atmosphere. The primary role of air is to make the planet suitable for breathing and the being of living organisms.
Nitrogen gas occupies a large office of the air. However, the chemic composition of the remaining part is exciting and varied. In short, the list of essential elements is as follows:
- Oxygen. The proportion of oxygen gas in the air fluctuates around 21% by book and 23% by mass. Together with nitrogen, these two gases course 99% of all Earth'south Air.
- Argon. Argon is odorless, colorless, and tasteless. A significant biological part of this gas has not been identified, but it has a narcotic issue and is even considered doping.
- Carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide makes up the atmosphere of Venus and Mars. Its per centum in the Earth's air is much lower. At the same time, a considerable amount of carbon dioxide is independent in the ocean. In solid form, carbon dioxide is one of the best-known dry ice refrigerants.
- Neon. Neon has a narcotic effect on a person at a certain pressure, but information technology is platonic gas used in the grooming of divers and other people working under full pressure.
- Methane. Today, this gas, produced and used equally a fuel and raw material in production, is not equally widespread in the temper, only it still escapes from the Earth.
- Helium. This gas is not amidst the most important in terms of importance. Information technology is difficult to make up one's mind the biological significance of this gas.
- Krypton. Krypton is an inert gas iii times heavier than air, chemically inert, extracted from the air, used in incandescent lamps, lasers and is still being actively studied.
- Hydroge n. Hydrogen atoms in the air occupy 0,00005% by volume and 0,00008% past mass, simply at the aforementioned fourth dimension, they are the most mutual elements in the Universe.
- Xenon.Nowadays, people cannot do without xenon: the production of powerful and pulsed lite sources, diagnostics and anesthesia in medicine, spacecraft engines, rocket fuel.
Air Density
What is the density of air? The density of a gas can be analytically determined by dividing its mass past the volume it occupies under given conditions (air pressure, absolute temperature, and humidity). You can also calculate its density using the ideal gas police: pV = nRT, where n is gas molecules, R is the gas constant. Thus, information technology is necessary to know the absolute pressure level and temperature of the air and its gas constant and mole fraction. This equation calculates the dry density of air.
Water Vapor
Due to the evaporation of water from the ocean's surface, moist air is always present in the air. The amount of humid air depends on the air temperature, the presence and speed of the wind, the nature of the relief, the vegetation cover, and the soil's color.
According to Dalton's law, air pressure containing water vapor is the sum of the pressure of dry air and the pressure of h2o vapor. Atmospheric pressure is: Pa = Pda + Pp.
The humidity of the air can exist judged either by the magnitude of the pressure level produced by the steam. The corporeality of water vapor contained in 1 m3 of air is chosen accented humidity. The ratio of water vapor density at a given temperature to the saturated vapor density at the same temperature is chosen relative humidity.
Air Properties
Air has many properties, and you lot need to know about these:
- The air is transparent, colorless, odorless, and does not conduct estrus well.
- Air conducts sunlight well.
- Air takes up infinite in the surrounding world.
- Air tin can exist compressed.
- Air is rubberband.
- Air expands when heated; when cooled, air contracts.
Warm air is lighter than cold air and tends upward.
Molar Mass Of Dry Ice,
Source: https://studybay.com/blog/molar-mass-of-air/
Posted by: verdugolanny1979.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Molar Mass Of Dry Ice"
Post a Comment